Features
Constitutions and amendments
By Neville Ladduwahetty
The 20th Amendment (20A) to the Constitution has become a topic of spirited debate and discussion. Much of it is generated by misunderstanding the true intent of 20A. It should not be a durable amendment to the Constitution. Instead, it should be temporary, until a comprehensive new Constitution is developed and presented to the nation.
Until then, 20A should serve as a stop gap for the Executive President to address the unprecedented challenges the country has to face following the COVID-19 pandemic. With this in mind, the intent of 20A should be to either repeal those provisions that had been introduced by the 19th Amendment to seriously dilute executive powers as admitted by the framers of 19A or to repeal 19A altogether and restore the executive powers the President had under the 1978 Constitution. It is only by removing the constraints that exist under 19A that the President would be in a position to address the daunting challenges that lie ahead. Without strengthening the hand of the Executive, the formidable task of social and economic recovery that the country is compelled to face because of the global pandemic would be a near impossibility.
THE NEED for 20A
The two most formidable issues that should engage the full attention of the government and the nation are:
(1) The need to continue with the very effective measures adopted to contain COVID-19 in order to prevent the possibility of a resurgance.
(2) The absolute urgency to revive the seriously depressed economy, brought about nationally and globally by the pandemic.
As far as the first issue is concerned, the government has demonstrated very effectively that it has the capabilities and organizing abilities to implement procedures and practices to maintain the health of the nation to such a degree that the President and the Sri Lankan nation have received international acclaim. An equally encouraging aspect is the support extended by the public to the call of the government to practice the health safeguards recommended by the government. What the government and the nation have collectively achieved is a shining example to the world for which we as a nation could be proud of.
The elephant in the room is how to revive the depressed economy. While the measures that need to be adopted are bound to test the skills and ingenuities of the entire nation, an equally important factor that would have a direct bearing is the freedom for the government, in particular the President and the executive branch, to act without being constrained by the fetters introduced by 19A.
There is no denying the fact that 19A was introduced with the deliberate intent of diluting executive powers of the President. In fact, Dr. Jayampathy Wickramaratne P.C., (Dr. JW) referring to 19A, has admitted that the initial attempt was “to completely abolish the Presidential system of government”. This attempt failed because the Supreme Court ruled that the intended attempt would require a referendum. The end result was the compromised version of 19A. According to Dr. JW, “The experience under 19A clearly showed the need to completely abolish the Presidential form of government and move towards a Parliamentary form…” (The Island, September 8, 2020).
The approach should not be to analyze which Article should be amended and to what degree, since such an exercise would not only be time consuming but also would add to the confusion that already exists in 19A. Instead, the approach should be to undo the entirety of 19A, and for the executive power of the President that had existed under the 1978 Constitution to be restored, for the simple reason that tough measures are needed to overcome the economic black hole Sri Lanka is in, the likes of which the nation as a whole has never seen.
The argument that such an approach would restore what is often described as draconian executive power amounting to a Presidential dictatorship that had existed under the 1978 Constitution, is unfounded if one realizes the full impact of the economic catastrophe the nation is currently facing. The situation is so dire that the bulk of the nation is more concerned with the basics of existence and survival rather than about niceties of Democracy and Good Governance that only the fortunate few could afford to be concerned about.
THE NEED for a NEW CONSTITUTION
Having addressed the short term issues, the next is the long term issue of a new Constitution. The genesis for 19A and 20A is the 1978 Constitution. Therefore, any anomalies and contradictions that exist in amendments invariably are a result of anomalies and contradictions in the 1978 Constitution. Describing the system of government under the 1978 Constitution, Dr. JW quotes Dr. Colvin R. De Silva as having described the 1978 Constitution “as a constitutional presidential dictatorship dressed in the raiment of a parliamentary democracy’ (Ibid). The comment is justified because the 1978 Constitution has features of Presidential and Parliamentary systems, notwithstanding that each represents one of the two ideologically completely different systems of government by which practically all democracies are governed. If such contrasting systems are incorporated in a single constitution confusion is inevitable, as evident from the 1978 Constitution and its related amendments. Therefore, the framers of a new constitution should endeavour to base it on either one or the other, a Presidential or a Parliamentary system, but certainly not a mix of both.
PARLIAMENTARY and PRESIDENTIAL
FORMS of GOVERNMENT
Under a Parliamentary system, Parliament is supreme and as described in the 1972 Constitution is the “supreme instrument of State Power”. This means that Parliament is responsible for Legislative and Executive functions. A few members of Parliament are selected by the Prime Minister to form the Cabinet of Ministers to exercise the executive functions of the government. Consequently, the Cabinet of Ministers is responsible and answerable to Parliament.
On the other hand, under a Presidential system, the cardinal principle is the separation of Legislative and Executive power. This separation is underscored by the fact that each branch is separately elected by the people and responsible for the exercise of separate powers, namely Legislative and Executive. This separation is clearly outlined in Articles 4 (a) and 4 (b) respectively, of the 1978 Constitution.
Article 4 (a) states: “the legislative power of the People shall be exercised by parliament…”.
Article 4 (b) states: “the executive power of the People, including the defence of Sri Lanka, shall be exercised by the President…”.
Commenting on the executive power of the people, the Supreme Court in S.D. No. 04/2015 stated: “It is in this background that the Court in the Nineteenth Amendment Determination came to a conclusion that the transfer, relinquishment or removal of the power attributed to one organ of government to another organ or body would be inconsistent with Article 3 read with Article 4 of the Constitution. Though Article 4 provides the form and manner of the sovereignty of the people, the ultimate act or decision of the executive functions must be retained by the President. So long as the President remains the Head of the Executive, the exercise of his powers remain supreme or sovereign in the executive field and to others to whom such power is given must derive the authority from the President or exercise the Executive power vested in the President as a delegate of the President”.
On the other hand, Article 43 (1) states: “There shall be a Cabinet of Ministers charged with the direction and control of the Government of the Republic which shall be collectively responsible and answerable to Parliament”.
Commenting on Article 43 (1) the Supreme Court in the same case, S.D. No. 04/2015 stated: “This important Article underscores that the Cabinet collectively is charged with the exercise of Executive power, which is expressed as the direction and control of the Government of the Republic and the collective responsibility of Cabinet of which the President is the Head. It establishes conclusively that the President is not the sole repository of Executive power under the Constitution. It is the Cabinet of Ministers collectively, and not the President alone, which is charged with the direction and control of the Government.
This Cabinet is answerable to Parliament. Therefore, the Constitution itself recognizes that Executive power is exercised by the President and by the Cabinet of Ministers, and that the President shall be responsible to Parliament and the Cabinet of Ministers, collectively responsible and answerable to Parliament with regard to the exercise of such powers…”.
It is evident from the opinions cited above that the powers of the President depend on whether he acts under provisions of Article 4 (b) or Article 43 (1). For instance, under provisions of 4 (b) the “President as the Head of the Executive is sovereign in the executive field”. However, if the President acts under provisions of Article 43 (1) the Court stated that “the Constitution itself recognizes that Executive power is exercised by the President and by the Cabinet of Ministers”. The potential for such contrasting interpretations that exist in the 1978 Constitution have been blindly repeated in 19A without regard for their relevance or irrelevance.
Another serious contradiction often overlooked is that a President elected by the People should be recognized as being co-equal with Parliament under provisions of separation of power. Therefore, the President cannot be responsible to another organ of government– the Parliament. Furthermore, if the Cabinet of Ministers derive their authority from the President as interpreted by the Supreme Court, the Cabinet cannot be responsible and answerable to Parliament either. Under the circumstances, Article 33A that calls for the President to be responsible to Parliament “for the due exercise performance and discharge of his powers, duties and functions” is a violation of the principle of separation of power.
The few examples cited above amply demonstrate that while the framework of the 1978 Constitution is essentially Presidential, it has sufficient elements of a Parliamentary Democracy to warrant the Judiciary from giving contrasting opinions depending on which Article it interprets. This ambiguity requires Sri Lanka to adopt either a Presidential or a Parliamentary system, but not a mix of both systems. Despite the fact that such contradictions have been brought to the attention of the public, confusion has reigned uninterrupted. Therefore, the need is for Parliament to vote on which system of government is best suited to govern Sri Lanka. Furthermore, when formulating a new constitution, it is also recommended that a fresh approach be incorporated to devolve power to the smallest practical workable unit in order to strengthen operations in the periphery.
CONCLUSION
According to media reports the intention of the government is to introduce the 20th Amendment. Indications are that each Article would be reviewed and amended where necessary. Such an exercise is bound to repeat the contradictions in 19A because the framers mechanically copied provisions from the 1978 Constitution without understanding what separation of power is all about in a Presidential system. Therefore, it is best to repeal 19A completely, and go back to the powers exercised by the President under the 1978 Constitution as a stop gap measure until a new constitution is formulated. Such an interim measure is vital in order to prevent a resurgence of COVID-19 and to equip the executive with necessary powers to revive the depressed economy.
Critics to such an approach may consider it to be the death knell to Parliamentary democracy. What such critics forget is that the country is in such dire straits economically, that drastic measures need to be introduced if the country is to get back to some degree of normalcy. Proof of the merits of such an approach is evident from the uncompromising measures successfully adopted by the government to contain COVID-19; a fact acknowledged internationally. The reversal to the past is intended to be only until such time that a new constitution is tabled and adopted by Parliament and the People at a referendum.
In summary, the essence of the recommendation is for the 20A to define a clear two-step approach. Step One is to repeal all of 19A and strengthen the hand of the President and the executive with necessary powers to address all issues relating to COVID-19, and to also adopt all necessary measures to revive the economy. Step Two is for Parliament to vote and give clear direction as to whether the new constitution should be based on a Presidential or Parliamentary system to address all issues relating to good governance in all respects. Adopting such a clear cut approach without ambiguities would enable Sri Lanka to be free of the current fog of confusion, and embark on a fresh Chapter in her history.
- News Advertiesment
See Kapruka’s top selling online shopping categories such as Toys, Grocery, Flowers, Birthday Cakes, Fruits, Chocolates, Clothing and Electronics. Also see Kapruka’s unique online services such as Money Remittence,News, Courier/Delivery, Food Delivery and over 700 top brands. Also get products from Amazon & Ebay via Kapruka Gloabal Shop into Sri Lanka.
Features
Islamophobia and the threat to democratic development

There’s an ill more dangerous and pervasive than the Coronavirus that’s currently sweeping Sri Lanka. That is the fear to express one’s convictions. Across the public sector of the country in particular many persons holding high office are stringently regulating and controlling the voices of their consciences and this bodes ill for all and the country.
The corrupting impact of fear was discussed in this column a couple of weeks ago when dealing with the military coup in Myanmar. It stands to the enduring credit of ousted Myanmarese Head of Government Aung San Suu Kyi that she, perhaps for the first time in the history of modern political thought, singled out fear, and not power, as the principal cause of corruption within the individual; powerful or otherwise.
To be sure, power corrupts but the corrupting impact of fear is graver and more devastating. For instance, the fear in a person holding ministerial office or in a senior public sector official, that he would lose position and power as a result of speaking out his convictions and sincere beliefs on matters of the first importance, would lead to a country’s ills going unaddressed and uncorrected.
Besides, the individual concerned would be devaluing himself in the eyes of all irrevocably and revealing himself to be a person who would be willing to compromise his moral integrity for petty worldly gain or a ‘mess of pottage’. This happens all the while in Lankan public life. Some of those who have wielded and are wielding immense power in Sri Lanka leave very much to be desired from these standards.
It could be said that fear has prevented Sri Lanka from growing in every vital respect over the decades and has earned for itself the notoriety of being a directionless country.
 All these ills and more are contained in the current controversy in Sri Lanka over the disposal of the bodies of Covid victims, for example. The Sri Lankan polity has no choice but to abide by scientific advice on this question. Since authorities of the standing of even the WHO have declared that the burial of the bodies of those dying of Covid could not prove to be injurious to the wider public, the Sri Lankan health authorities could go ahead and sanction the burying of the bodies concerned. What’s preventing the local authorities from taking this course since they claim to be on the side of science? Who or what are they fearing? This is the issue that’s crying out to be probed and answered.
All these ills and more are contained in the current controversy in Sri Lanka over the disposal of the bodies of Covid victims, for example. The Sri Lankan polity has no choice but to abide by scientific advice on this question. Since authorities of the standing of even the WHO have declared that the burial of the bodies of those dying of Covid could not prove to be injurious to the wider public, the Sri Lankan health authorities could go ahead and sanction the burying of the bodies concerned. What’s preventing the local authorities from taking this course since they claim to be on the side of science? Who or what are they fearing? This is the issue that’s crying out to be probed and answered.
Considering the need for absolute truthfulness and honesty on the part of all relevant persons and quarters in matters such as these, the latter have no choice but to resign from their positions if they are prevented from following the dictates of their consciences. If they are firmly convinced that burials could bring no harm, they are obliged to take up the position that burials should be allowed.
If any ‘higher authority’ is preventing them from allowing burials, our ministers and officials are conscience-bound to renounce their positions in protest, rather than behave compromisingly and engage in ‘double think’ and ‘double talk’. By adopting the latter course they are helping none but keeping the country in a state of chronic uncertainty, which is a handy recipe for social instabiliy and division.
In the Sri Lankan context, the failure on the part of the quarters that matter to follow scientific advice on the burials question could result in the aggravation of Islamophobia, or hatred of the practitioners of Islam, in the country. Sri Lanka could do without this latter phobia and hatred on account of its implications for national stability and development. The 30 year war against separatist forces was all about the prevention by military means of ‘nation-breaking’. The disastrous results for Sri Lanka from this war are continuing to weigh it down and are part of the international offensive against Sri Lanka in the UNHCR.
However, Islamophobia is an almost world wide phenomenon. It was greatly strengthened during Donald Trump’s presidential tenure in the US. While in office Trump resorted to the divisive ruling strategy of quite a few populist authoritarian rulers of the South. Essentially, the manoeuvre is to divide and rule by pandering to the racial prejudices of majority communities.
It has happened continually in Sri Lanka. In the initial post-independence years and for several decades after, it was a case of some populist politicians of the South whipping-up anti-Tamil sentiments. Some Tamil politicians did likewise in respect of the majority community. No doubt, both such quarters have done Sri Lanka immeasurable harm. By failing to follow scientific advice on the burial question and by not doing what is right, Sri Lanka’s current authorities are opening themselves to the charge that they are pandering to religious extremists among the majority community.
The murderous, destructive course of action adopted by some extremist sections among Muslim communities world wide, including of course Sri Lanka, has not earned the condemnation it deserves from moderate Muslims who make-up the preponderant majority in the Muslim community. It is up to moderate opinion in the latter collectivity to come out more strongly and persuasively against religious extremists in their midst. It will prove to have a cementing and unifying impact among communities.
It is not sufficiently appreciated by governments in the global South in particular that by voicing for religious and racial unity and by working consistently towards it, they would be strengthening democratic development, which is an essential condition for a country’s growth in all senses.
A ‘divided house’ is doomed to fall; this is the lesson of history. ‘National security’ cannot be had without human security and peaceful living among communities is central to the latter. There cannot be any ‘double talk’ or ‘politically correct’ opinions on this question. Truth and falsehood are the only valid categories of thought and speech.
Those in authority everywhere claiming to be democratic need to adopt a scientific outlook on this issue as well. Studies conducted on plural societies in South Asia, for example, reveal that the promotion of friendly, cordial ties among communities invariably brings about healing among estranged groups and produces social peace. This is the truth that is waiting to be acted upon.
Features
Pakistan’s love of Sri Lanka

By Sanjeewa Jayaweera
It was on 3rd January 1972 that our family arrived in Karachi from Moscow. Our departure from Moscow had been delayed for a few weeks due to the military confrontation between Pakistan and India. It ended on 16th December 1971. After that, international flights were not permitted for some time.
The contrast between Moscow and Karachi was unbelievable. First and foremost, Moscow’s temperature was near minus 40 degrees centigrade, while in Karachi, it was sunny and a warm 28 degrees centigrade. However, what struck us most was the extreme warmth with which the airport authorities greeted our family. As my father was a diplomat, we were quickly ushered to the airport’s VIP Lounge. We were in transit on our way to Rawalpindi, the airport serving the capital of Islamabad.
We quickly realized that the word “we are from Sri Lanka” opened all doors just as saying “open sesame” gained entry to Aladdin’s cave! The broad smile, extreme courtesy, and genuine warmth we received from the Pakistani people were unbelievable.
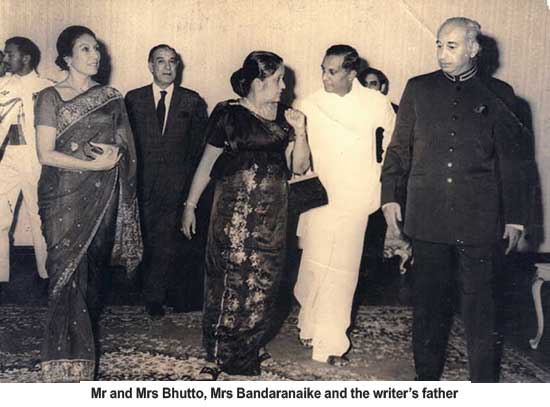
This was all to do with Mrs Sirima Bandaranaike’s decision to allow Pakistani aircraft to land in Colombo to refuel on the way to Dhaka in East Pakistan during the military confrontation between Pakistan and India. It was a brave decision by Mrs Bandaranaike (Mrs B), and the successive governments and Sri Lanka people are still enjoying the fruits of it. Pakistan has been a steadfast and loyal supporter of our country. They have come to our assistance time and again in times of great need when many have turned their back on us. They have indeed been an “all-weather” friend of our country.
Getting back to 1972, I was an early beneficiary of Pakistani people’s love for Sri Lankans. I failed the entrance exam to gain entry to the only English medium school in Islamabad! However, when I met the Principal, along with my father, he said, “Sanjeewa, although you failed the entrance exam, I will this time make an exception as Sri Lankans are our dear friends.” After that, the joke around the family dinner table was that I owed my education in Pakistan to Mrs B!
At school, my brother and I were extended a warm welcome and always greeted “our good friends from Sri Lanka.” I felt when playing cricket for our college; our runs were cheered more loudly than of others.
One particular incident that I remember well was when the Embassy received a telex from the Foreign inistry. It requested that our High Commissioner seek an immediate meeting with the Prime Minister of Pakistan, Mr Zulifikar Ali Bhutto (ZB), and convey a message from Mrs B. The message requested that an urgent shipment of rice be dispatched to Sri Lanka as there would be an imminent rice shortage. As the Ambassador was not in the station, the responsibility devolved on my father.
It usually takes about a week or more to get an audience with the Prime Minister (PM) of a foreign country due to their busy schedule. However, given the urgency, my father spoke to the Foreign Ministry’s Permanent Sectary, who fortunately was our neighbour and sought an urgent appointment. My father received a call from the PM’s secretary around 10 P.M asking him to come over to the PM’s residence. My father met ZB around midnight. ZB was about to retire to bed and, as such, was in his pyjamas and gown enjoying a cigar! He had greeted my father and had asked, “Mr Jayaweera, what can we do for great friend Madam Bandaranaike?. My father conveyed the message from Colombo and quietly mentioned that there would be riots in the country if there is no rice!
ZB had immediately got the Food Commissioner of Pakistan on the line and said, “I want a shipload of rice to be in Colombo within the next 72 hours!” The Food Commissioner reverted within a few minutes, saying that nothing was available and the last export shipment had left the port only a few hours ago to another country. ZB had instructed to turn the ship around and send it to Colombo. This despite protests from the Food Commissioner about terms and conditions of the Letter of Credit prohibiting non-delivery. Sri Lanka got its delivery of rice!
The next was the visit of Mrs B to Pakistan. On arrival in Rawalpindi airport, she was given a hero’s welcome, which Pakistan had previously only offered to President Gaddafi of Libya, who financially backed Pakistan with his oil money. That day, I missed school and accompanied my parents to the airport. On our way, we witnessed thousands of people had gathered by the roadside to welcome Mrs B.
When we walked to the airport’s tarmac, thousands of people were standing in temporary stands waving Sri Lanka and Pakistan flags and chanting “Sri Lanka Pakistan Zindabad.” The noise emanating from the crowd was as loud and passionate as the cheering that the Pakistani cricket team received during a test match. It was electric!
I believe she was only the second head of state given the privilege of addressing both assemblies of Parliament. The other being Gaddafi. There was genuine affection from Mrs B amongst the people of Pakistan.
I always remember the indefatigable efforts of Mr Abdul Haffez Kardar, a cabinet minister and the President of the Pakistan Cricket Board. From around 1973 onwards, he passionately championed Sri Lanka’s cause to be admitted as a full member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) and granted test status. Every year, he would propose at the ICC’s annual meeting, but England and Australia’s veto kept us out until 1981.
I always felt that our Cricket Board made a mistake by not inviting Pakistan to play our inaugural test match. We should have appreciated Mr Kardar and Pakistan’s efforts. In 1974 the Pakistan board invited our team for a tour involving three test matches and a few first-class games. Most of those who played in our first test match was part of that tour, and no doubt gained significant exposure playing against a highly talented Pakistani team.
Several Pakistani greats were part of the Pakistan and India team that played a match soon after the Central Bank bomb in Colombo to prove that it was safe to play cricket in Colombo. It was a magnificent gesture by both Pakistan and India. Our greatest cricket triumph was in Pakistan when we won the World Cup in 1996. I am sure the players and those who watched the match on TV will remember the passionate support our team received that night from the Pakistani crowd. It was like playing at home!
I also recall reading about how the Pakistani government air freighted several Multi Barrell artillery guns and ammunition to Sri Lanka when the A rmy camp in Jaffna was under severe threat from the LTTE. This was even more important than the shipload of rice that ZB sent. This was crucial as most other countries refused to sell arms to our country during the war.
Time and again, Pakistan has steadfastly supported our country’s cause at the UNHCR. No doubt this year, too, their diplomats will work tirelessly to assist our country.
We extend a warm welcome to Mr Imran Khan, the Prime Minister of Pakistan. He is a truly inspirational individual who was undoubtedly an excellent cricketer. Since retirement from cricket, he has decided to get involved in politics, and after several years of patiently building up his support base, he won the last parliamentary elections. I hope that just as much as he galvanized Sri Lankan cricketers, his political journey would act as a catalyst for people like Kumar Sangakkara and Mahela Jayawardene to get involved in politics. Cricket has been called a “gentleman’s game.” Whilst politics is far from it!.
Features
Covid-19 health rules disregarded at entertainment venues?

Believe me, seeing certain videos, on social media, depicting action, on the dance floor, at some of these entertainment venues, got me wondering whether this Coronavirus pandemic is REAL!
To those having a good time, at these particular venues, and, I guess, the management, as well, what the world is experiencing now doesn’t seem to be their concerned.
Obviously, such irresponsible behaviour could create more problems for those who are battling to halt the spread of Covid-19, and the new viriant of Covid, in our part of the world.
The videos, on display, on social media, show certain venues, packed to capacity – with hardly anyone wearing a mask, and social distancing…only a dream..
How can one think of social distancing while gyrating, on a dance floor, that is over crowded!
If this trend continues, it wouldn’t be a surprise if Coronavirus makes its presence felt…at such venues.
And, then, what happens to the entertainment scene, and those involved in this field, especially the musicians? No work, whatsoever!
Lots of countries have closed nightclubs, and venues, where people gather, in order to curtail the spread of this deadly virus that has already claimed the lives of thousands.
Thailand did it and the country is still having lots of restrictions, where entertainment is concerned, and that is probably the reason why Thailand has been able to control the spread of the Coronavirus.
With a population of over 69 million, they have had (so far), a little over 25,000 cases, and 83 deaths, while we, with a population of around 21 million, have over 80,000 cases, and more than 450 deaths.
I’m not saying we should do away with entertainment – totally – but we need to follow a format, connected with the ‘new normal,’ where masks and social distancing are mandatory requirements at these venues. And, dancing, I believe, should be banned, at least temporarily, as one can’t maintain the required social distance, while on the dance floor, especially after drinks.
Police spokesman DIG Ajith Rohana keeps emphasising, on TV, radio, and in the newspapers, the need to adhere to the health regulations, now in force, and that those who fail to do so would be penalised.
He has also stated that plainclothes officers would move around to apprehend such offenders.
Perhaps, he should instruct his officers to pay surprise visits to some of these entertainment venues.
He would certainly have more than a bus load of offenders to be whisked off for PCR/Rapid Antigen tests!
I need to quote what Dr. H.T. Wickremasinghe said in his article, published in The Island of Tuesday, February 16th, 2021:
“…let me conclude, while emphasising the need to continue our general public health measures, such as wearing masks, social distancing, and avoiding crowded gatherings, to reduce the risk of contact with an infected person.
“There is no science to beat common sense.”
But…do some of our folks have this thing called COMMON SENSE!










