Opinion
Religion, end to discord?

Imagine that your religion, like most religions, does not consider changing faith as a punishable offence – say, Buddhism. If one of your family members changed her religion, for example, to Hindu, but continued to live the same good life she had been living till then, would you have any objections regarding her change of faith? Is it likely that you would condemn her for what you call a disloyalty of sorts?
There is no reason why you should feel bad about it unless you think that changing one’s ‘faith’ is improper. If this family member starts living an immoral life after changing track, you have reason to be worried. However, if she does not show any decline in her conduct, you have no basis for worry unless you are unjustly biased against anyone changing one’s religion. However, most families, irrespective of their faith, would at least try their best to dissuade her from taking up a new faith. And, surely, the resistance of the family would depend on various factors including the intensity of your faith in your religion, the levels as well as the nature of education of the family members, your general outlook on life, how open-minded you are about sensitive issues and the binding nature of the decrees of your religion. The pressure your family would bring to bear on the nonconforming member would be the net result of all these factors.
If the majority were more tolerant the objection from the family is likely to be minimal and the ‘rebel’ would make the transition with no loss of face. Further, the less stringent your religion was regarding codes of discipline, the less disquieting the defection would be for everybody concerned. Now, think of a whole family changing faith. The situation would be equally disconcerting, or much worse this time, for they would incur the displeasure of a larger religious community, be it neighbours, friends or relatives. The disapproval would once again depend on the factors mentioned above and, perhaps, more. Besides, their displeasure, if not censure, would be immediate and, what’s more, it would certainly not come from any fear of the nonconformist family becoming immoral.
However, this sort of negative reaction flies in the face of what we are frequently made to believe about the civilizing nature of all established religions. Priests and laymen tell us frequently that all religions are set to make us behave more virtuously and hence we should not show any disregard to other religions. This sounds great. If these claims were genuine, no one – priest or layman – could have any difficulty whatsoever in readily consenting to any person of any faith switching allegiance at any point in his life. Sam Harris, the neuroscientist, philosopher and writer expresses the same sentiments more pointedly and with no trace of ostentation when he says, “Just as there is no such thing as Christian physics or Muslim algebra, we will see that there is no such thing as Christian or Muslim morality” (The Moral Landscape). In sum, morals are useful recommendations for good conduct no matter whichever religion you inherited from your parents. It’s a plea for scores of humans who remain haplessly divided by historical circumstances despite their capacity to agree on codes of behaviour based on love and compassion, which we all are capable of feeling, whichever religion we were initiated into as children by circumstances.
Suppose, religion, at its best, is a way of helping people to realize their best selves, through which they can maximize their sense of togetherness, collective well-being and happiness. As we may all agree, morals prescribed by any religion can stand on their own without reference to other religions. This is true of all religions, be it Christianity, Buddhism, Islam, etc. What if one were to ask why not distil the morals of all the religions practiced in your society and formulate a common schema agreeable to all? He would say that it would enable our next generation to live in a society which will not be compartmentalized by religions imposed on them by their parents whom they didn’t choose. However, such a proposition would be summarily dismissed by many of those who profess the uniqueness of each religion. Why?
The reason is, for an overwhelming majority of us religion is much more than a manual for a good life. In addition to the ethical aspect, there is, in every religion, an intricate web of worldly as well as supernatural features that engage us both physically and emotionally. Ninian Smart in his book The Religious Experience of Mankind sums up the many-sidedness of religion when he says, “it is a six dimensional organism, typically containing doctrines, myths, ethical teachings, rituals and social institutions, and animated by religious experiences of various kinds.” As the title of the book indicates, the ‘experiential’ element plays a significant role in tying us to our religion. It seems that the bewildering variety of all the above features of religion that creates the deep divisive lines between one religion and another, which we cannot circumvent easily despite our efforts to bring about religious reconciliation. Ironically, this goes against the avowed mission of all religions to make the world a better place for all humans. Our obsession with the ‘other world’ enunciated, differently, by each religion eclipses the brotherhood they seek to promote. This is sad, isn’t it? However much we reject it, don’t we have the deep-rooted feeling that our religion holds the key to truth and ‘ultimate salvation’ and thus the moral precepts of our religion have more authority compared with those of other religions? Our early indoctrination makes us feel reluctant to look at ethics as useful and modifiable standards of behaviour. It is not open-mindedness but an attitude of insularity and fussiness that robs us of the opportunity of uniting under one banner.
Let’s take the following scenario to help us understand our self-indulgent blinkeredness more objectively. Imagine that all living beings and plants were to be wiped out from this earth one of these days either by a chemical mishap or a much more virulent pandemic than the current one. It will perhaps take millions of years for intelligent beings to evolve again on earth. They will never have heard of any of our religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Hindu, Islam, etc. However, they are sure to develop their respective religions that are likely to interpret things like good and bad which could not be detached from their irreconcilable interpretations of ‘after life.’ Now, being millions of years distanced from them, we would be able to better understand their predicament as ‘outsiders’ without sharing their emotional attachments to their religions. What advice can we offer them to make their world a place of less turmoil? The best instruction would be to urge them to formulate their morals free of religious tones so that they would avoid endless frictions that are likely to lead to disunity and enmity. We may tell them that morals work best without religious stamps on them, if our experiences are anything to go by.
Now take the train back to the present moment. If example is better than precept, what will be our first step towards a more peaceful world? It will be to encourage people to, firstly, understand the applicability of morals devoid of their religious flavour and, secondly, go easy on the non-verifiable and mutually exclusive claims about ‘after life.’ Will science be able to help us in this project?
Although science has constantly been taking over spaces occupied by magic and religion in the past, many people remain pessimistic about science ever coming to throw light on ‘after life.’ However, Yuval Noah Harari, renowned historian and philosopher, says, “In premodern times religions were responsible for solving a wide range of technical problems in mundane fields such as agriculture…when an agricultural crisis loomed…, farmers turned to the priests to intercede with the gods. Medicine too fell within the religious domain… if you were ill you were likely to go to the witch doctor rather than to the doctor…” (21 Lessons for the 21st Century)
Surely, unlike our ancestors, we are far too enlightened to trust religion any longer to solve our day to day problems. However, with regard to ‘after life’ we don’t seem to be that much better informed than our ancient cousins. As such, the confusion about what happens after death has caused human beings the world over to be more divided than united. All religions, as we said previously, claim to know the ultimate truth about where we would ‘go’ after death. As religions don’t rely on empirical methods of verification of this claim, it is unlikely that they will be any wiser in this regard even in the next millennium. Let’s hope science will throw some light on the issue sooner than later and save us from being divided on the basis of unverified claims till the cows come home. If consensus on ethics can unite us why let unearthly and nebulous issues thwart it?
Susantha Hewa
- News Advertiesment
See Kapruka’s top selling online shopping categories such as Toys, Grocery, Flowers, Birthday Cakes, Fruits, Chocolates, Clothing and Electronics. Also see Kapruka’s unique online services such as Money Remittence,News, Courier/Delivery, Food Delivery and over 700 top brands. Also get products from Amazon & Ebay via Kapruka Gloabal Shop into Sri Lanka.
Opinion
Take Human Rights seriously, not so much the council or office

By Dr Laksiri Fernando
The 46th Session of the UN Human Rights Council started on 22 February morning with obvious hiccups. The Office, to mean the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, finally decided to hold all sessions virtually online, only the President of the Council and the assistants in the high table sitting at the UN Assembly Hall in Geneva. The President, Ms. Nazhat Shammen Khan, Ambassador from Fiji in Geneva, wearing a saree, was graceful in the chair with empty seats surrounding.
In the opening session, the UN General Assembly President, UN General Secretary, UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, and Head of Foreign Affairs, Switzerland (as the host country), addressed remotely the session. In fact, there was no need for Switzerland to have a special place, as the UN is independent from any host country. Switzerland is fairly ok, however, if this tradition is followed, the UN General Assembly may have to give a special place to the US in New York.
Initial Addresses
UN General Secretary, Antonio Guterres’ address could have been quite exemplary if he gave a proper balance to the developed and developing countries. He talked about racism and fight against racism but did not mention where racism is overwhelmingly rampant (US and Europe) and what to do about it. Outlining the human rights implications of Covid-19 pandemic, he made quite a good analysis. It was nice for him to say, ‘human rights are our blood line (equality), our lifeline (for peace) and our frontline (to fight against violations).’ However, in the fight against violations, he apparently forgot about the ‘blood line’ or the ‘lifeline’ quite necessary not to aggravate situations through partiality and bias. He never talked about the importance of human rights education or promoting human rights awareness in all countries.
His final assault was on Myanmar. Although he did not call ‘genocide,’ he denounced the treatment of Rohingyas as ethnic cleansing without mentioning any terrorist group/s within. His call for the release of Aung San Suu Kyi and other civilian leaders undoubtedly should be a common call of all. However, he did not leave any opening for a dialogue with the military leaders or bring back a dialogue between Aung San and Min Aung, the military leader. With a proper mediation, it is not impossible. Calling for a complete overhaul as the young demonstrators idealistically claim might not be realistic.
 High Commissioner Michelle Bachelet’s address was brief and uncontroversial this time without mentioning any country or region. It is clear by now perhaps she is not the real author of the Report against Sri Lanka, but someone probably hired by the so-called core-group led by Britain. Her major points were related to the coronavirus pandemic trying to highlight some of the socio-economic disparities and imbalances of policy making that have emerged as a result. The neglect of women, minorities, and the marginalized sections of society were emphasized. But the poor was not mentioned. As a former medical doctor, she also opted to highlight some of the medical issues underpinning the crisis.
High Commissioner Michelle Bachelet’s address was brief and uncontroversial this time without mentioning any country or region. It is clear by now perhaps she is not the real author of the Report against Sri Lanka, but someone probably hired by the so-called core-group led by Britain. Her major points were related to the coronavirus pandemic trying to highlight some of the socio-economic disparities and imbalances of policy making that have emerged as a result. The neglect of women, minorities, and the marginalized sections of society were emphasized. But the poor was not mentioned. As a former medical doctor, she also opted to highlight some of the medical issues underpinning the crisis.
Then came the statements from different countries in the first meeting in the following order: Uzbekistan, Colombia, Lithuania, Afghanistan, Poland, Venezuela, Finland, Fiji, Moldova, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Equatorial Guinea, Vietnam, Belgium, and Morocco. The obvious purposes of these statements were different. Some countries were apparently canvassing for getting into the Human Rights Council at the next turn perhaps for the purpose of prestige. Some others were playing regional politics against their perceived enemies. This was very clear when Lithuania and Poland started attacking Russia.
But there were very sincere human rights presentations as well. One was the statement by the President of Afghanistan, Mohammad Ashraf Ghani. He outlined the devastating effects that Afghanistan had to undergo during the last 40 years, because of foreign interferences. The initial support to Taliban by big powers was hinted. His kind appeal was to the UN was to go ‘beyond discourse to practice’ giving equal chance to the poor and the developing countries to involve without discrimination.
Controversial Presentations
China’s Foreign Affairs Minister, Wang Yi, made his presentation almost at the end of the first day. This is apparently the first time that China had directly addressed the Human Rights Council. Beginning with outlining the devastating repercussions of the coronavirus pandemic he stressed that the world should face the challenges through ‘solidarity and cooperation.’ He broadened the concept to human rights solidarity and cooperation. His expressed views were quite different to the others, particularly to the Western ones.
He frankly said that what he expresses are the views of China on human rights without claiming those are absolute truths or forcing others to believe or implement them. There were four main concepts that he put forward before the member countries. First, he said, “We should embrace a human rights philosophy that centres on the people. The people’s interests are where the human rights cause starts and ends.” Second, he said, “we should uphold both universality and particularity of human rights. Peace, development, equity, justice, democracy, and freedom are common values shared by all humanity and recognized by all countries.” “On the other hand,” he said, “countries must promote and protect human rights in light of their national realities and the needs of their people.”
“Third,” he said, “we should systemically advance all aspects of human rights. Human rights are an all-encompassing concept. They include civil and political rights as well as economic, social, and cultural rights.” He then emphasized, “Among them, the rights to subsistence and development are the basic human rights of paramount importance.” Fourth, “we should continue to promote international dialogue and cooperation on human rights. Global human rights governance should be advanced through consultation among all countries.”
It was on the same first day before China, that the United Kingdom launched its barrage against several countries not sparing Sri Lanka. The Foreign Secretary, Dominic Raab, delivered the statement from top to bottom attacking alleged violating countries on human rights. But there was no mentioning of Israel for the repression of Palestinians or the systemic racism rampaging in the United States, including the 6 January attacks on the Capitol by extremist/terrorist groups.
His first sermon was on Myanmar without acknowledging the British atrocities or mismanagement of this poor and diverse country during the colonial period. He was quite jubilant over implementing sanctions and other restrictions over the country. Many sanctions, in my opinion, are extortions. Undoubtedly, Aung San Suu Kyi and other leaders should be released, and democracy restored. This is a task of the whole council and when one or two countries try to grab the credit, there can be obvious reservations of others.
His further scathing attacks were against Belarus, Russia, and China. Some appeared factually correct but not necessarily the approach or the motives genuine. The following is the way he came around Sri Lanka. He said,
“Finally, we will continue to lead action in this Council: on Syria, as we do at each session; on South Sudan; and on Sri Lanka, where we will present a new resolution to maintain the focus on reconciliation and on accountability.”
‘Action’ to him basically means repeatedly passing resolutions, of course imposing economic and other sanctions. He said, “as we do at each session”; like bullying poor or weak countries at each session. Can there be a resolution against Russia or China? I doubt it.
What would be the purpose of presenting a resolution against Sri Lanka? As he said, “to maintain the focus on reconciliation and on accountability.” This will satisfy neither the Tamil militants nor the Sinhalese masses. But it might satisfy the crafty Opposition (proxy of the defeated last government). This is not going to be based on any of the actual measures that Sri Lanka has taken or not taken on reconciliation or accountability. But based on the ‘Authoritarian and Hypocritical Report’ that some anti-Sri Lankans have drafted within the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. This what I have discussed in my last article.
In this context, successful or not, the statement made by the Sri Lanka’s Minister of External Affairs, Dinesh Gunawardena, in rejecting any resolution based on the foxy Report of the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, in my concerned opinion, is absolutely correct.
Opinion
President’s energy directives ignored by the Power Ministry: Another Point of View

Dr Tilak Siyambalapitiya
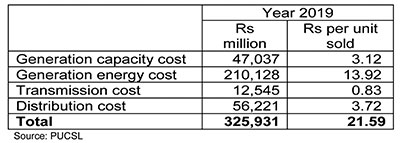
Dr Janaka Rathnasiri laments (The Island 19 Feb 2021) that the Power Ministry has ignored the President’s directive to draw 70% of energy from renewable sources by 2030. I saw the approved costs of electricity production for 2019, published by the Public Utilities Commission (PUCSL).
PUCSL has also approved the prices to sell electricity to customers. Although various customers pay at various “approved” prices, the average income from such “approved” prices in 2019 was Rs 17.02 per unit. It is not only the Ministry, according to Dr Rathnasiri, ignoring the President; PUCSL is also breaking the law, which says prices and approved costs should be equal.
 So there is already an illegal gap of Rs 21.59 minus 17.02 = Rs 4.57 per unit of electricity sold. If electricity prices are not to be increased, as stated by many in the government and PUCSL, let us say the following: Distribution costs should decrease by 0.57 Rs per unit. Generation costs should decrease by Rs 4.00 per unit.
So there is already an illegal gap of Rs 21.59 minus 17.02 = Rs 4.57 per unit of electricity sold. If electricity prices are not to be increased, as stated by many in the government and PUCSL, let us say the following: Distribution costs should decrease by 0.57 Rs per unit. Generation costs should decrease by Rs 4.00 per unit.
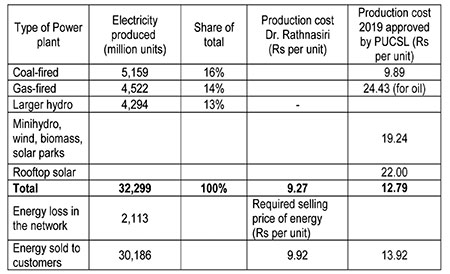
PUCSL also published the approved cost of purchasing or producing electricity from various sources for 2019. The actual energy values were different to what was approved, but let us stick to PUCSL approved figures:
I suggest Dr Rathnasiri fills-up the following table, to show how much electricity will cost in 2030 to produce and deliver, if the President’s 70% target is to be achieved and for PUCSL to abide by the law. Let us assume that electricity requirement in 2030 will be double that of 2019.
 Since PUCSL has to save Rs 4 from 13.92, the average selling price for energy should be Rs 13.92 minus 4.00 = Rs 9.92. With a target network loss of 7% (in 2019 it was 8.4%), the average cost of production has to be Rs 9.27 per unit. Eight cages have to be filled-up by Dr Rathnasiri.
Since PUCSL has to save Rs 4 from 13.92, the average selling price for energy should be Rs 13.92 minus 4.00 = Rs 9.92. With a target network loss of 7% (in 2019 it was 8.4%), the average cost of production has to be Rs 9.27 per unit. Eight cages have to be filled-up by Dr Rathnasiri.
In 2012, PUCSL approved the energy cost of electricity produced from coal power to be 6.33 Rs per kWh. In 2019, PUCSL approved 9.89 (56% increase). For renewable energy, it was 13.69 in 2012, and 19.24 in 2019 (a 40% increase, but double the price of electricity from coal fired generation). In 2012, rooftop solar was not paid for: only give and take, but now paid Rs 22, against Rs 9.89 from coal. There seems to be something wrong. The price reductions of renewable energy being promised, being insulated from rupee depreciation, are not happening? Either Sri Lanka must be paying too little for coal, or it may be renewable energy is severely over-priced?
On coal we hear only of some corruption every now and then; so Sri Lanka cannot be paying less than it costs, for coal.
Enough money even to donate
vaccines
 Another reason for the Ministry of Power to ignore the President’s directive may be the Ministry’s previous experience with similar Presidential directives. In 2015, the President at that time cancelled the Sampur coal-fired power plant, and the Ministry faithfully obliged. That President and that Prime Minister then played ball games with more power plants until they were thrown out of power, leaving a two-billion-dollar deficit (still increasing) in the power sector. Not a single power plant of any description was built.
Another reason for the Ministry of Power to ignore the President’s directive may be the Ministry’s previous experience with similar Presidential directives. In 2015, the President at that time cancelled the Sampur coal-fired power plant, and the Ministry faithfully obliged. That President and that Prime Minister then played ball games with more power plants until they were thrown out of power, leaving a two-billion-dollar deficit (still increasing) in the power sector. Not a single power plant of any description was built.
Where is this deficit? You do not have to look far. In the second table, replace 24.43 with 9.89, to reflect what would have happened if Sampur was allowed to be built. The value 12.79 will go down to 8.55, well below the target of Rs 9.27 per unit to produce. Not only would CEB and LECO report profits, but the government too could have asked for an overdraft from CEB to tide over any cash shortfalls in the treasury. All this with no increase in customer prices. Producers of electricity from renewable energy could enjoy the price of 19.24 Rs per unit. And that blooming thing on your rooftop can continue to enjoy Rs 22 per unit. The Minister of Power, whom Dr Rathnasiri wants to replace with an army officer, would have been the happiest.
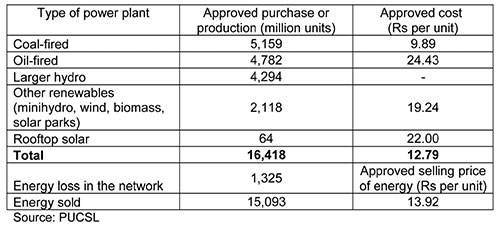 In the absence of Sampur (PUCSL’s letter signed by Chairman Saliya Mathew confirmed cancellation and asked CEB not to build it), PUCSL approved electricity to be produced at Rs 21.59 and sold at Rs 17.02 per unit. The annual loss would be Rs (21.59 – 17.02) x 15,093 = Rs 69 billion per year of approved financial loss. Sri Lanka has a Telecom regulator, an Insurance regulator, a Banking regulator, who never approve prices below costs. Sometime ago the telecom regulator asked the operators to raise the prices, when operators were proposing to reduce prices amidst a price war. But the electricity industry regulator is different: he approves costs amounting to 27% more than the price, not just once but, but continuously for ten long years !
In the absence of Sampur (PUCSL’s letter signed by Chairman Saliya Mathew confirmed cancellation and asked CEB not to build it), PUCSL approved electricity to be produced at Rs 21.59 and sold at Rs 17.02 per unit. The annual loss would be Rs (21.59 – 17.02) x 15,093 = Rs 69 billion per year of approved financial loss. Sri Lanka has a Telecom regulator, an Insurance regulator, a Banking regulator, who never approve prices below costs. Sometime ago the telecom regulator asked the operators to raise the prices, when operators were proposing to reduce prices amidst a price war. But the electricity industry regulator is different: he approves costs amounting to 27% more than the price, not just once but, but continuously for ten long years !
That is 370 million dollars per year as of 2019, the economy is spending, and for years to come, to burn oil (and say we have saved the environment). Did the Minister of Health say we are short of 160 million dollars to buy 40 million doses of the vaccine? Well, being a former Minister of Power, she now knows which Presidential “order” of 2015 is bleeding the economy of 370 million dollars per year, adequate to buy all vaccines and donate an equal amount to a needy country.
Prices are the production costs approved by PUCSL for 2019. The selling price approved by the same PUCSL was Rs 9.27 per unit.
Opinion
Confusion on NGOs and NSOs in Sri Lanka

If you listen to politicians and journalists here, you will hear of that curious creature rajya novana sanvidane, a Non-State Organization (NSO). Where do you get them? In the uninstructed and dead minds of those who use those terms. In the real world, where politicians and journalists have developed minds, there are Non-Governmental Organizations (NGO). The United Nations is an organization set up by state parties, not by governments. It is true that agents of states, governments, make the United Nations work or fail. Governments may change but not the states, except rarely. When Eritrea broke away from Ethiopia, a new state was formed and was so recognised by the United Nations. However, the LTTE that tried to set up another state was crushed by the established state that it tried to break away from, and the UN had nothing to do with them.
This entirely unnecessary confusion, created out of ignorance, is so destructive that organizations completely loyal to the existing state, are made to be traitorous outfits, for they are ‘non-state organizations’ within the state. There are citizens of each state, but no citizens of any government. Government is but an instrument of the state. In most states there are organizations, neither of the state nor of government: religious organizations including churches. But none of them is beyond the pale of the state.
Those that speak of rajya novana sanvidane give that name partly because they have no idea of the origin of non-governmental organizations. NGOs came into the limelight, as donor agencies, noticed that some governments, in East Africa, in particular, did not have the capacity and the integrity to use the resources that they provided. They construed, about 1970, that NGOs would be a solution to the problem. Little did they realize that some NGOs themselves would become dens of thieves and brigands. I have not seen any evaluation of the performance of NGOs in any country. There was an incomplete essay written by Dr. Susantha Gunatilleka. NGOs are alternatives to the government, not to the state.
Our Constitution emphatically draws a distinction between the government and state, and lays down that the President is both Head of Government and Head of State (Read Article 2 and Article 30 of the Constitution.) It is as head of state that, he/she is the Commander of the Armed Forces, appoints and receives ambassadors and addresses Parliament annually, when a prorogued Parliament, reconvenes. He/she presides over the Cabinet as head of government. The distinction is most clear, in practice, in Britain where Queen Elizabeth is the head of state and Boris Johnson is the Prime Minister and head of government. However, in principle, Johnson is the Queen’s First Minister appointed by the sovereign, and resigns by advising her of his decision to do so.
In the US and in India the term ‘state’ has special significance. In India there is a ‘rajya sabha’ (the Council of States) whose members represent constituent States and Union Territories. Pretty much the same is true of the United States. In the US, executive power is vested in the President and heads the administration, government in our parlance. The Head of State does not come into the Constitution but those functions that one associates with a head of state are in the US performed by the President of the Republic. The US President does not speak of my state (mage rajaya) but of my administration, (mage anduva). Annually, he addresses Congress on the State of the Union. Our present President must be entirely familiar with all this, having lived there as a citizen of the US for over a decade. It is baffling when someone speaks of a past state as a traitor to that same state. It is probable that a government was a traitor to the state. ‘Treason against the United States, shall consist only in levying war against them, or in adhering to their (States’) enemies, giving them aid and comfort’. That a state was a traitor to the same state is gobbledygook.
Apart from probable confusion that we spoke of in the previous paragraph, it is probable that a president and other members of a government, including members of the governing party here, find it grandiloquent to speak of his/her/their state (mage/ape rajaya), rather than my government (mage anduva) or Sirisena anduva’ and not Sirisena state; it was common to talk of ‘ape anduva’ in 1956; politicians in 1956 were far more literate then than they are now.
When translating from another language, make sure that you understand a bit of the history of the concept that you translate. A public school in the US is not the same as a public school in the UK.
MAHADENAMUTTA









