Midweek Review
Understanding the role of Foreign Direct Investment in port development: A Pathfinder Brief
Private sector involvement in developing ports became a critical necessity in the 1980s due to a host of reasons. The bottleneck effect caused due to congestion in ports, had a considerable strain on the efficiency of distribution chains, which is an important factor that needed attention.
In this backdrop, government investments into port development were seen as a “White Elephant Syndrome”.
Amplified by recurring port congestion, consequent chronic service failures, were mainly attributed to the deterioration of service quality during this period.
Inadequate port services are phenomenal in this context, owing to the inability of governments to invest in port infrastructure capable of catering to the needs of international shipping. Hence many port complexes became virtual “white elephants”.
Secondly, the centralized control by the governments in the port sector hindered adequate responses to overwhelming demands. Particularly during the 1960s to 1980, central planning in the port sector and elsewhere prevailed in the socialist economies and in many western and developing countries where state-held ports were often promoted by international development banks
The third, was the restrictive labour practices, and the denial of institutional reform and technological advances that frequently precede rapid modernization of port handling equipment. Initially, labour unions often refused to accept reductions in the workforce, ignoring the need to upgrade skills.
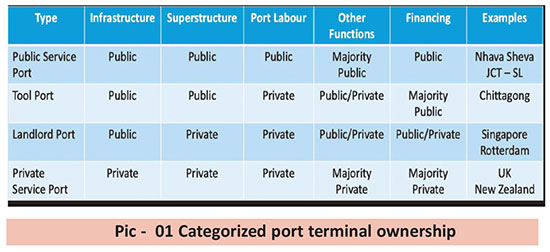
The World Bank has classified Port Terminal Ownership and Administration into 4 models based on public private partnership.
(See pic – 01)
The opportunity of gaining a share in the Indian subcontinent transhipment market in post-Covid recovery
Transhipment emerged in the 1970s as trade with Asia increased. However, volumes were not sufficient to justify direct connections to many ports, in Asia. Nevertheless, Kaohsiung emerged as the first transhipment hub. As container ships grew larger on improved designs setting up of pure transhipment hubs along major shipping routes, including Colombo, became a necessity.
The Colombo Port expansion project was funded by the ADB owing to the country’s ailing domestic economy. In ADB’s 2007 report, the rationale for the expansion is stated as “Colombo Port is the natural transhipment hub for the South Asian region. However, in recent years Colombo Port lost its market share in the regional transhipment market because the fundamentals of the market changed, and Colombo Port did not adapt. Colombo Port cannot offer the additional operating capacity required to compete for the Indian subcontinent transhipment market or the depth required to berth the latest generation container ships. Colombo Port will have to develop additional container berths with the required depth to address this capacity and depth infrastructure constraints if it is to remain a transhipment hub port.” Transhipment and India’s Contribution towards Hub Status of the Colombo Port is a fact that cannot be ignored.

(See pic – 02)
South Asia has suffered the most during the pandemic with a 10% dip in forecasted volumes. The region will play catch-up in the years to come.

(See pic – 03)
Meanwhile, Singapore has lost its top slot to Shanghai in the last 14 years. Zhoushan, Shenzen and Guanzhou have been developed as very close competitors to Singapore. Growth in these new ports was driven by Chinese economic growth. Similarly, Sri Lanka cannot ignore the growth in the Indian economy. IMF projected India to grow by 11.5% in 2021 and Sri Lanka is well positioned to benefit from this growth.
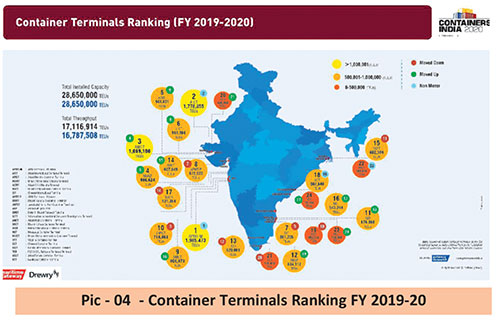
(See pic – 04)
India has 12 major ports and around 200 non-major ports. In FY20, major ports in India handled 704.82 million metric tonnes (MMT) of cargo. Cargo traffic at non-major ports reached 447.21 MMT in FY20. Since ports handle almost 95% of the trade volumes in India, the rising trade has contributed significantly to the country’s cargo traffic. Given the positive outlook, proposed investment in major ports was expected to reach US$ 18.6 billion by 2020, while those in non-major ports, around US$ 28.5 billion.
Indian transhipment is the main business of the Port of Colombo. With Terminals being developed, the total capacity of Colombo can be projected to an estimated 14-15 Mn TEU’s annually. As of now 85% of this will be transhipment containers, over 70% of which will be to/from India, hence Colombo cannot discount the relevance of India, to remain as a prospective hub Port. As explained initially, transhipment hubs were created as domestic economies were unable to sustain longer shipping routes. In this backdrop, what we need to realise is that expansion of the Colombo Port is unsustainable in the absence of Indian transhipment containers.
Fundamentals of Port Business – Importance of Links between Port Operators and Shipping Lines
Major Port operators have established links with main shipping lines to plan routes, which are strategically important to shipping lines. The shipping lines schedule their routes considering the services and pricing offered by the Port Operators. This and a host of other reasons compel governments to refrain from ports development, including inability and lack of flexibility to attract main shipping lines. These are vital factors that Sri Lanka seems to have ignored in its decision to develop the East Container Terminal.
The top 10 terminal operators with their respective market shares in 2019
.
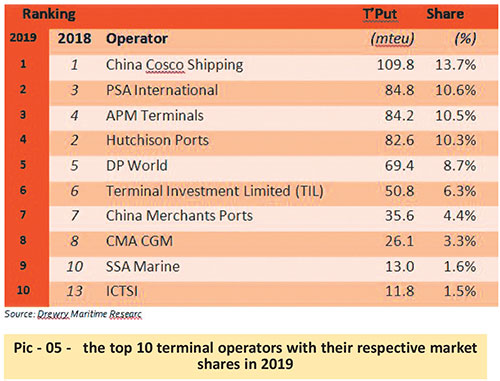
(See pic – 05)
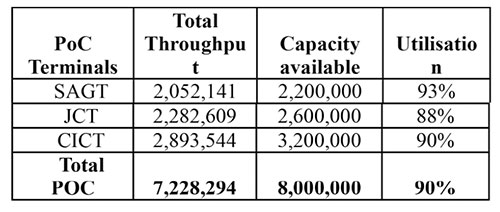
The Port of Colombo has reached its capacity and losing market share
Calendar Year 2019 (Jan – Dec) volume of terminals in the Port of Colombo (“POC”) compared against their respective capacities:
As of 2018-2019 we have reached the maximum capacity levels and had failed to gain an annual increase of at least 5-6% of transhipment volume, undoubtedly lost to regional peers.
Shippers’ Academy Colombo’s CEO Rohan Masakorala in his article published in the Daily FT captioned “Shipping and Ports in crisis”, clearly articulates an opportunity cost of 10% growth in transhipment volume lost due to delays in developing the ECT.
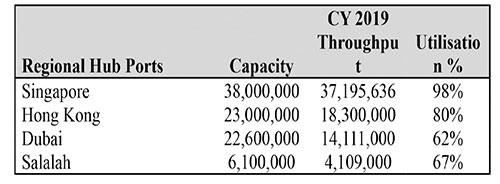
Capacities of other regional hubs and their utilization levels during 2019
ECT was to be operational by 2017 which would have added approx. 3 million TEUs annually to the POC capacity. Sri Lanka has lost a golden opportunity to capture marketshare due to inconsistent government Policy. The Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) completed development of the first phase of ECT by early 2015. This consisted of a 600m length quay wall, part container yard and a 440m deep-water berth. In 2016 a request for a proposal was floated to develop ECT on a BOT basis. This was terminated in 2017 when the GOSL contracted with India and Japan to develop the ECT. Based on these discussions, a MOC was signed in May 2019. This was overturned in February 2021 to develop ECT as a public service port.
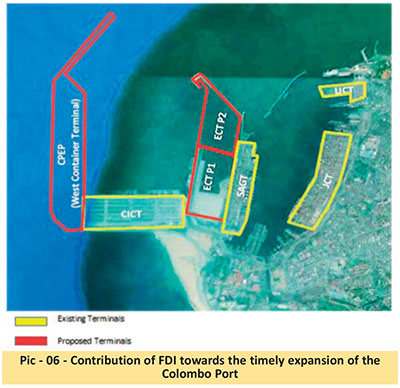
Contribution of FDI towards the timely expansion of the Colombo Port
Only 20% of the ECT has been developed up to now. It can service only 200,000 TEU’s annually at its best now. An investment of another US$ 550 million is required to develop the ECT to handle 3 million TEU’s annually. This needs to be done immediately to develop the terminal within two years. Duration is crucial in maintaining market share for the entire port. FDI is the need of the hour. It brings a package of capital and also market access and technology transfer will ensure timely development without stressing the GOSL financially. The GOSL will find it very challenging to invest US$ 550 mn to develop ECT based on their financial capability. Only time will tell if the decision to develop ECT as a public service port would be implemented in a timely and cost-effective manner, as articulated by the Trade Unions.
On a positive note, the GOSL’s initiative to hold discussions with India and Japan to develop the Western Container Terminal (WCT) as a private service port on a 35-year concession is a welcome change under these circumstances.
(See pic – 06)
The fulllength Pathfinder Brief is available at . Readers’ comments welcome to pm@pathfinderfoundation.org
- News Advertiesment
See Kapruka’s top selling online shopping categories such as Toys, Grocery, Flowers, Birthday Cakes, Fruits, Chocolates, Clothing and Electronics. Also see Kapruka’s unique online services such as Money Remittence,News, Courier/Delivery, Food Delivery and over 700 top brands. Also get products from Amazon & Ebay via Kapruka Gloabal Shop into Sri Lanka.
Midweek Review
‘Professor of English Language Teaching’

It is a pleasure to be here today, when the University resumes postgraduate work in English and Education which we first embarked on over 20 years ago. The presence of a Professor on English Language Teaching from Kelaniya makes clear that the concept has now been mainstreamed, which is a cause for great satisfaction.
 Twenty years ago, this was not the case. Our initiative was looked at askance, as indeed was the initiative which Prof. Arjuna Aluwihare engaged in as UGC Chairman to make degrees in English more widely available. Those were the days in which the three established Departments of English in the University system, at Peradeniya and Kelaniya and Colombo, were unbelievably conservative. Their contempt for his efforts made him turn to Sri Jayewardenepura, which did not even have a Department of English then and only offered it as one amongst three subjects for a General Degree.
Twenty years ago, this was not the case. Our initiative was looked at askance, as indeed was the initiative which Prof. Arjuna Aluwihare engaged in as UGC Chairman to make degrees in English more widely available. Those were the days in which the three established Departments of English in the University system, at Peradeniya and Kelaniya and Colombo, were unbelievably conservative. Their contempt for his efforts made him turn to Sri Jayewardenepura, which did not even have a Department of English then and only offered it as one amongst three subjects for a General Degree.
Ironically, the most dogmatic defence of this exclusivity came from Colombo, where the pioneer in English teaching had been Prof. Chitra Wickramasuriya, whose expertise was, in fact, in English teaching. But her successor, when I tried to suggest reforms, told me proudly that their graduates could go on to do postgraduate degrees at Cambridge. I suppose that, for generations brought up on idolization of E. F. C. Ludowyke, that was the acme of intellectual achievement.
I should note that the sort of idealization of Ludowyke, the then academic establishment engaged in was unfair to a very broadminded man. It was the Kelaniya establishment that claimed that he ‘maintained high standards, but was rarefied and Eurocentric and had an inhibiting effect on creative writing’. This was quite preposterous coming from someone who removed all Sri Lankan and other post-colonial writing from an Advanced Level English syllabus. That syllabus, I should mention, began with Jacobean poetry about the cherry-cheeked charms of Englishwomen. And such a characterization of Ludowyke totally ignored his roots in Sri Lanka, his work in drama which helped Sarachchandra so much, and his writing including ‘Those Long Afternoons’, which I am delighted that a former Sabaragamuwa student, C K Jayanetti, hopes to resurrect.
I have gone at some length into the situation in the nineties because I notice that your syllabus includes in the very first semester study of ‘Paradigms in Sri Lankan English Education’. This is an excellent idea, something which we did not have in our long-ago syllabus. But that was perhaps understandable since there was little to study then except a history of increasing exclusivity, and a betrayal of the excuse for getting the additional funding those English Departments received. They claimed to be developing teachers of English for the nation; complete nonsense, since those who were knowledgeable about cherries ripening in a face were not likely to move to rural areas in Sri Lanka to teach English. It was left to the products of Aluwihare’s initiative to undertake that task.
Another absurdity of that period, which seems so far away now, was resistance to training for teaching within the university system. When I restarted English medium education in the state system in Sri Lanka, in 2001, and realized what an uphill struggle it was to find competent teachers, I wrote to all the universities asking that they introduce modules in teacher training. I met condign refusal from all except, I should note with continuing gratitude, from the University of Sri Jayewardenepura, where Paru Nagasunderam introduced it for the external degree. When I started that degree, I had taken a leaf out of Kelaniya’s book and, in addition to English Literature and English Language, taught as two separate subjects given the language development needs of students, made the third subject Classics. But in time I realized that was not at all useful. Thankfully, that left a hole which ELT filled admirably at the turn of the century.
The title of your keynote speaker today, Professor of English Language Teaching, is clear evidence of how far we have come from those distant days, and how thankful we should be that a new generation of practical academics such as her and Dinali Fernando at Kelaniya, Chitra Jayatilleke and Madhubhashini Ratnayake at USJP and the lively lot at the Postgraduate Institute of English at the Open University are now making the running. I hope Sabaragamuwa under its current team will once again take its former place at the forefront of innovation.
To get back to your curriculum, I have been asked to teach for the paper on Advanced Reading and Writing in English. I worried about this at first since it is a very long time since I have taught, and I feel the old energy and enthusiasm are rapidly fading. But having seen the care with which the syllabus has been designed, I thought I should try to revive my flagging capabilities.
However, I have suggested that the university prescribe a textbook for this course since I think it is essential, if the rounded reading prescribed is to be done, that students should have ready access to a range of material. One of the reasons I began while at the British Council an intensive programme of publications was that students did not read round their texts. If a novel was prescribed, they read that novel and nothing more. If particular poems were prescribed, they read those poems and nothing more. This was especially damaging in the latter case since the more one read of any poet the more one understood what he was expressing.
Though given the short notice I could not prepare anything, I remembered a series of school textbooks I had been asked to prepare about 15 years ago by International Book House for what were termed international schools offering the local syllabus in the English medium. Obviously, the appalling textbooks produced by the Ministry of Education in those days for the rather primitive English syllabus were unsuitable for students with more advanced English. So, I put together more sophisticated readers which proved popular. I was heartened too by a very positive review of these by Dinali Fernando, now at Kelaniya, whose approach to students has always been both sympathetic and practical.
I hope then that, in addition to the texts from the book that I will discuss, students will read other texts in the book. In addition to poetry and fiction the book has texts on politics and history and law and international relations, about which one would hope postgraduate students would want some basic understanding.
Similarly, I do hope whoever teaches about Paradigms in English Education will prescribe a textbook so that students will understand more about what has been going on. Unfortunately, there has been little published about this but at least some students will I think benefit from my book on English and Education: In Search of Equity and Excellence? which Godage & Bros brought out in 2016. And then there was Lakmahal Justified: Taking English to the People, which came out in 2018, though that covers other topics too and only particular chapters will be relevant.
The former book is bulky but I believe it is entertaining as well. So, to conclude I will quote from it, to show what should not be done in Education and English. For instance, it is heartening that you are concerned with ‘social integration, co-existence and intercultural harmony’ and that you want to encourage ‘sensitivity towards different cultural and linguistic identities’. But for heaven’s sake do not do it as the NIE did several years ago in exaggerating differences. In those dark days, they produced textbooks which declared that ‘Muslims are better known as heavy eaters and have introduced many tasty dishes to the country. Watalappam and Buriani are some of these dishes. A distinguished feature of the Muslims is that they sit on the floor and eat food from a single plate to show their brotherhood. They eat string hoppers and hoppers for breakfast. They have rice and curry for lunch and dinner.’ The Sinhalese have ‘three hearty meals a day’ and ‘The ladies wear the saree with a difference and it is called the Kandyan saree’. Conversely, the Tamils ‘who live mainly in the northern and eastern provinces … speak the Tamil language with a heavy accent’ and ‘are a close-knit group with a heavy cultural background’’.
And for heaven’s sake do not train teachers by telling them that ‘Still the traditional ‘Transmission’ and the ‘Transaction’ roles are prevalent in the classroom. Due to the adverse standard of the school leavers, it has become necessary to develop the learning-teaching process. In the ‘Transmission’ role, the student is considered as someone who does not know anything and the teacher transmits knowledge to him or her. This inhibits the development of the student.
In the ‘Transaction’ role, the dialogue that the teacher starts with the students is the initial stage of this (whatever this might be). Thereafter, from the teacher to the class and from the class to the teacher, ideas flow and interaction between student-student too starts afterwards and turns into a dialogue. From known to unknown, simple to complex are initiated and for this to happen, the teacher starts questioning.’
And while avoiding such tedious jargon, please make sure their command of the language is better than to produce sentences such as these, or what was seen in an English text, again thankfully several years ago:
Read the story …
Hello! We are going to the zoo. “Do you like to join us” asked Sylvia. “Sorry, I can’t I’m going to the library now. Anyway, have a nice time” bye.
So Syliva went to the zoo with her parents. At the entrance her father bought tickets. First, they went to see the monkeys
She looked at a monkey. It made a funny face and started swinging Sylvia shouted: “He is swinging look now it is hanging from its tail its marvellous”
“Monkey usually do that’
I do hope your students will not hang from their tails as these monkeys do.
Midweek Review
Little known composers of classical super-hits

By Satyajith Andradi
Quite understandably, the world of classical music is dominated by the brand images of great composers. It is their compositions that we very often hear. Further, it is their life histories that we get to know. In fact, loads of information associated with great names starting with Beethoven, Bach and Mozart has become second nature to classical music aficionados. The classical music industry, comprising impresarios, music publishers, record companies, broadcasters, critics, and scholars, not to mention composers and performers, is largely responsible for this. However, it so happens that classical music lovers are from time to time pleasantly struck by the irresistible charm and beauty of classical pieces, the origins of which are little known, if not through and through obscure. Intriguingly, most of these musical gems happen to be classical super – hits. This article attempts to present some of these famous pieces and their little-known composers.
Pachelbel’s Canon in D
The highly popular piece known as Pachelbel’s Canon in D constitutes the first part of Johann Pachelbel’s ‘Canon and Gigue in D major for three violins and basso continuo’. The second part of the work, namely the gigue, is rarely performed. Pachelbel was a German organist and composer. He was born in Nuremburg in 1653, and was held in high esteem during his life time. He held many important musical posts including that of organist of the famed St Stephen’s Cathedral in Vienna. He was the teacher of Bach’s elder brother Johann Christoph. Bach held Pachelbel in high regard, and used his compositions as models during his formative years as a composer. Pachelbel died in Nuremburg in 1706.
Pachelbel’s Canon in D is an intricate piece of contrapuntal music. The melodic phrases played by one voice are strictly imitated by the other voices. Whilst the basso continuo constitutes a basso ostinato, the other three voices subject the original tune to tasteful variation. Although the canon was written for three violins and continuo, its immense popularity has resulted in the adoption of the piece to numerous other combinations of instruments. The music is intensely soothing and uplifting. Understandingly, it is widely played at joyous functions such as weddings.
Jeremiah Clarke’s Trumpet Voluntary
The hugely popular piece known as ‘Jeremiah Clarke’s Trumpet Voluntary’ appeared originally as ‘ The Prince of Denmark’s March’ in Jeremiah Clarke’s book ‘ Choice lessons for the Harpsichord and Spinet’, which was published in 1700 ( Michael Kennedy; Oxford Dictionary of Music ). Sometimes, it has also been erroneously attributed to England’s greatest composer Henry Purcell (1659 – 1695 ) and called ‘Purcell’s Trumpet Voluntary (Percy A. Scholes ; Oxford Companion to Music). This brilliant composition is often played at joyous occasions such as weddings and graduation ceremonies. Needless to say, it is a piece of processional music, par excellence. As its name suggests, it is probably best suited for solo trumpet and organ. However, it is often played for different combinations of instruments, with or without solo trumpet. It was composed by the English composer and organist Jeremiah Clarke.
Jeremiah Clarke was born in London in 1670. He was, like his elder contemporary Pachelbel, a musician of great repute during his time, and held important musical posts. He was the organist of London’s St. Paul’s Cathedral and the composer of the Theatre Royal. He died in London in 1707 due to self – inflicted gun – shot injuries, supposedly resulting from a failed love affair.
Albinoni’s Adagio
The full title of the hugely famous piece known as ‘Albinoni’s Adagio’ is ‘Adagio for organ and strings in G minor’. However, due to its enormous popularity, the piece has been arranged for numerous combinations of instruments. It is also rendered as an organ solo. The composition, which epitomizes pathos, is structured as a chaconne with a brooding bass, which reminds of the inevitability and ever presence of death. Nonetheless, there is no trace of despondency in this ethereal music. On the contrary, its intense euphony transcends the feeling of death and calms the soul. The composition has been attributed to the Italian composer Tomaso Albinoni (1671 – 1750), who was a contemporary of Bach and Handel. However, the authorship of the work is shrouded in mystery. Michael Kennedy notes: “The popular Adagio for organ and strings in G minor owes very little to Albinoni, having been constructed from a MS fragment by the twentieth century Italian musicologist Remo Giazotto, whose copyright it is” (Michael Kennedy; Oxford Dictionary of Music).
Boccherini’s Minuet
The classical super-hit known as ‘Boccherini’s Minuet’ is quite different from ‘Albinoni’s Adagio’. It is a short piece of absolutely delightful music. It was composed by the Italian cellist and composer Luigi Boccherini. It belongs to his string quintet in E major, Op. 13, No. 5. However, due to its immense popularity, the minuet is performed on different combinations of instruments.
Boccherini was born in Lucca in 1743. He was a contemporary of Haydn and Mozart, and an elder contemporary of Beethoven. He was a prolific composer. His music shows considerable affinity to that of Haydn. He lived in Madrid for a considerable part of his life, and was attached to the royal court of Spain as a chamber composer. Boccherini died in poverty in Madrid in 1805.
Like numerous other souls, I have found immense joy by listening to popular classical pieces like Pachelbel’s Canon in D, Jeremiah Clarke’s Trumpet Voluntary, Albinoni’s Adagio and Boccherini’s Minuet. They have often helped me to unwind and get over the stresses of daily life. Intriguingly, such music has also made me wonder how our world would have been if the likes of Bach, Handel, Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven, and Schubert had never lived. Surely, the world would have been immeasurably poorer without them. However, in all probability, we would have still had Pachelbel’s Canon in D, Jeremiah Clarke’s Trumpet Voluntary, Albinoni’s Adagio, and Boccherini’s Minuet, to cheer us up and uplift our spirits.
Midweek Review
The Tax Payer and the Tough

By Lynn Ockersz
The tax owed by him to Caesar,
Leaves our retiree aghast…
How is he to foot this bill,
With the few rupees,
He has scraped together over the months,
In a shrinking savings account,
While the fires in his crumbling hearth,
Come to a sputtering halt?
But in the suave villa next door,
Stands a hulk in shiny black and white,
Over a Member of the August House,
Keeping an eagle eye,
Lest the Rep of great renown,
Be besieged by petitioners,
Crying out for respite,
From worries in a hand-to-mouth life,
But this thought our retiree horrifies:
Aren’t his hard-earned rupees,
Merely fattening Caesar and his cohorts?









